Rita, Life Sciences Consultant at ALTEN, tells us more about the Pharmaceutical Industry’s qualification activities.
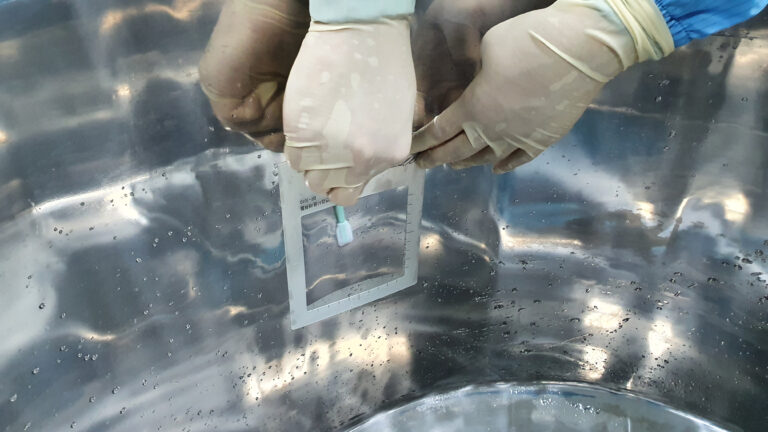
Pharmaceutical industry enhanced the execution, control and tracking of the tests done according to specifications/requirements necessaries for compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). The need and extent of Validation, Qualification and Commissioning are established taking into account applicable guidelines and International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE) approach to assure that new premises, equipment, utilities, systems, facilities, processes and procedures have been properly designed, installed, and tested according to pre-determined acceptance criteria, based on Impact Assessment of that installation, operational and performance characteristics, and parameters with potential impact on product quality. This is also applicable to the moment changes are made depending on the Risk Assessment or when required or indicated, based on the outcome of periodic review.
Validation is a systematic approach which aims to provide and document enough data to give a high degree of assurance and evidence. In this way, a process or an analytical method will consistently produce results within required specifications. Detailed in the User Requirement Specification (URS). When this approach is related to a system or equipment work correctly and lead to the expected results, this is referred to as Qualification. Which is part of, but not limited to, a Validation process, which in turn can be divided into:
- Design Qualification (DQ) is the documented verification that the proposed design of the system suits the intended purpose. In compliance with the applicable URS.
- Installation Qualification (IQ) is the documented verification that the system was correctly installed or modified. This must follow the approved design, manufacturer’s recommendations (if available) and with the applicable URS.
- Operation Qualification (OQ). It is the documented verification that the system and sub-systems perform as intended throughout all the defined operating ranges. In compliance with the applicable URS.
- Performance Qualification (PQ). It is the documented verification that a system performs effectively as expected under simulated real-world conditions, based on the approved process method and specifications.
In order to accomplish with a successful and simplified Qualification effort, a comprehensive plan must be developed, through the relationship and interdependency between Good Engineering Practice (GEP) and Commissioning phases and the Qualification phase(s) of the project. According to the complexity of the project, many documents can be generated. They describe plans and approaches as Change Control, URS, Validation Master Plan (VMP), Risk Analysis, Validation/Qualification Protocol, Validation/Qualification Report, and Deviations/ Corrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA), if necessary. Quality Unit must approve all Qualification and/or Validation documents before its execution.
After the execution of all Qualification and/or Validation activities, the systems Qualified or Validated can be considered closed and released for GMP use if:
- Quality Unit formally assesses and approves the failure of qualification or validation activities/test (derivation), regarding their potential impact on the system release for GMP manufacturing.
- Follow up actions are tracked in a Quality System (CAPA and/or Change Control) and all activities are closed.
- The required Qualification or Validation was successfully concluded.
Quality Assurance ensures that appropriate quality practices and procedures are adopted early in the project to guarantee that regulatory requirements and expectations are respected. Practical application of these requirements is the key to the efficient managing of Qualification activities.