In the pharmaceutical industry, the use of customized software for process control is the best way to guarantee the quality and integrity of drugs on a large scale. There are softwares that allow process control engineers to design and configure product recipes with several advantages. Better traceability, productivity, reproducibility, reduction of human error and process variability are some of the advantages that this software provides.
This software allows you to operate in two production modes, auto mode and batch mode. There is also the manual mode, but this does not imply the use of software, it only requires human action in all stages of drug production. The major disadvantages of this option are the increase of equipment use time, batch-to-batch product variability, risk of human error, and the reduction product quality.

Manual mode. Auto mode. Batch mode
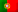
In auto mode, users follow the BPR (Batch procedure report) instructions to give commands (example: start and/or end of agitation operation, temperature, pressure control, etc.) and insert process parameter set points into the automation system. It requires human action to start, stop and monitor each necessary operation.
In batch mode, the automation system executes the operations following the sequence of the electronic batch recipe that is designed/configured by a process control engineer. The sequence of batch operations defines commands, setpoints, control and alarm parameters, waits until process conditions or user input is reached. Recipes also interact with the operator when necessary, releasing pop-ups at specific times to confirm some process conditions.
Batch mode increases productivity because the process is performed consistently, increases the operational efficiency, decreases the variability, human error records, operations, and paperwork. It also allows information sharing because all actions are automatically reported online and available by means of a batch report.
Batch recipe qualification steps
The batch recipe can be used to produce a drug after going through several qualification steps, namely:
- Define batch recipe structure. Define batch recipe structure with the three areas involved in its approval and qualification, namely, QA (Quality Assurance), AU (Automation) and UA (User area). It is responsibility of the process control engineer from the automation area to configure the batch recipe according to the process detailed in the BPR and to what was agreed with the 3 areas. After the batch recipe is configured, the 3 qualification steps are started: DQ (Design Qualification), IQ (Installation Qualification), OQ (Operational Qualification) and PQ (Performance Qualification).
- DQ. Review and approval of the batch recipe design by the 3 areas involved in the qualification (QA, AU and UA).
- IQ. After the DQ is approved, the ready code is imported from the virtual machine to the real system, where the recipe will be available to the user.
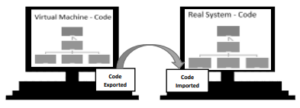
- OQ. After the IQ is approved, offline testing of the batch recipe can start. This test is done in a virtual machine where all the equipment and operations used in the production of the drug are realistically simulated. This test is essential to track any configuration errors or even the identification of some improvements in the equipment, avoiding loss of time in the production area. After carrying out the offline test and the respective corrections being implemented, the UA will run a “blank test” where the recipe is tested in a real environment with only solvent. If it is necessary to perform any corrections, these can only be implemented if they do not put in question the design of the batch recipe approved initially. In case there is any correction that compromises the design of the recipe, the DQ of the batch recipe must be approved again, as well as the other qualification steps already performed previously.
- PQ. After the OQ is approved, the batch recipe is used in the production of the drug. For PQ approval, at least 3 batches successfully produced using a batch recipe are required. After the PQ of the batch recipe is approved, it means that it is qualified and guarantees the quality of the product.
It is the responsibility of the process control engineer to implement and qualify batch recipes, train its users, support production during the manufacturing process, create and/or improve documentation and useful operations for the recipes (example: charge, discharge, agitation, pressure, temperature, recirculation, etc.). All the work performed by the process control engineer involves eliminating the root cause(s) of non-conformities (CAPA – Corrective action and Preventive action).

Post was written by Tania,
Process Engineer & Life Sciences Consultant